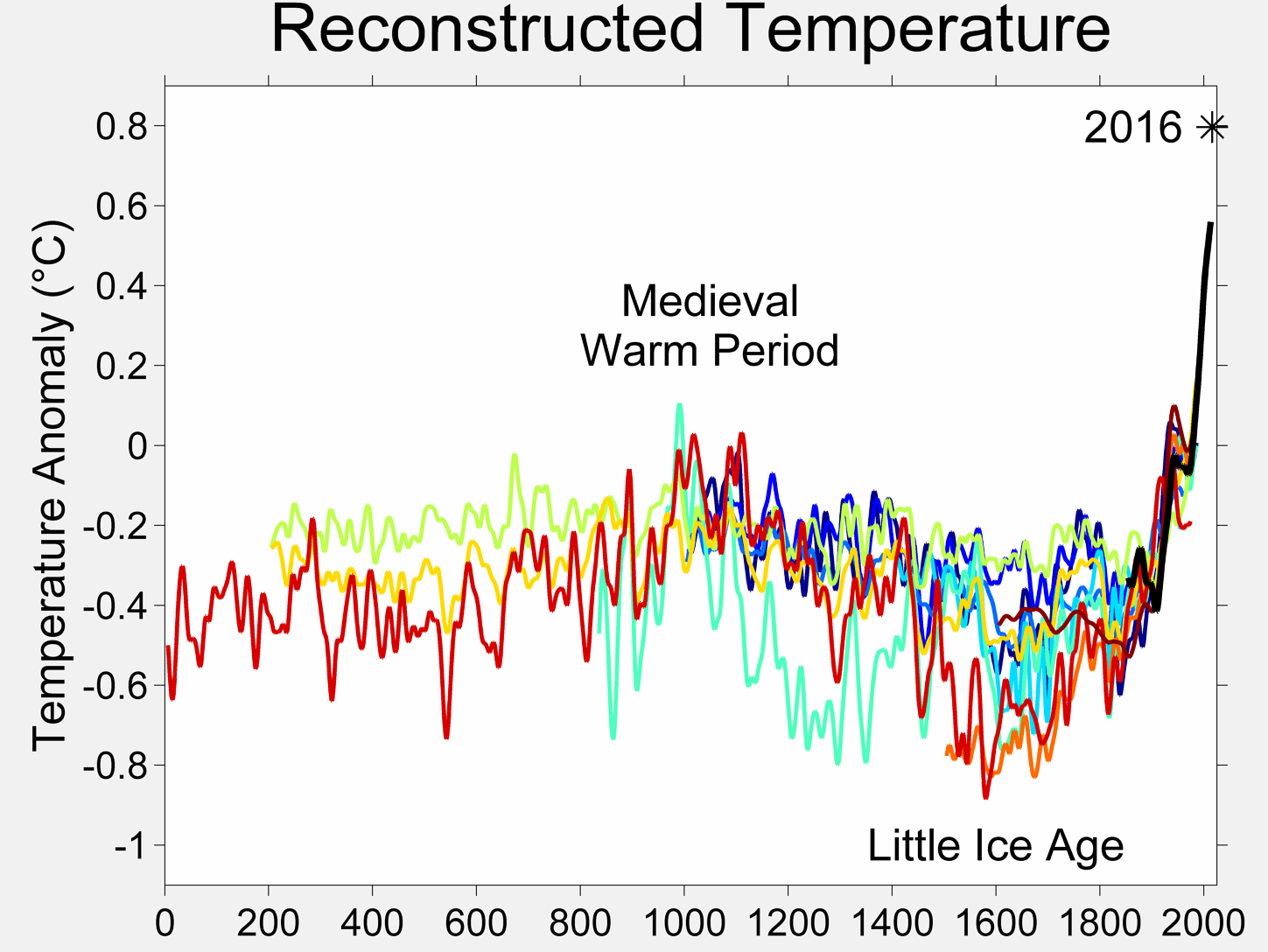
The Medieval Global Temperature Optimum was a time of warm climate in the North Alantic region from around 950 AD to 1250. This period showed notably warm weather in many parts of the world, mainly the North Atlantic, Southern Greenland, the Eurasian Arctic, and parts of North America. The sea temperature was approximately 1 degree warmer than today according to the radiocarbon-dated box core in the Sargasso Sea. Additionally, sediment samples were analyzed from different areas, indicating an increased amount of North Atlantic tropical cyclone activity. The warm climate was also evident through the settlement of Greenland and other northern lands by Vikings who could take advantage of the ice-free seas.
Following this period of abnormally warm climate, there was a period of cooler climate called the Little Ice Age. Although the period's dates cannot be defined, climatologists have noted three cold intervals between AD 1550 and 1850 which were separated by slight warming. The causes of the cold periods include cyclical lows in solar radiation, heightened volcanic activity, changes in the ocean circulation, and variability in general. There was an increase in mountain glacier formation outside Europe, such as Alaska, New Zealand, and Patagonia. Additionally, the time brought colder winters to parts of Europe and North America. Snowfall was much heavier in areas such as Portugal.